Weekly vs 3-weekly cisplatin: a retrospective cohort study
Purpose/Objective
To investigate the differences in outcome of CRT with three-weekly cisplatin (100mg/m², cis100) versus weekly (40mg/m², cis40) cisplatin in the treatment of locally advanced (LA) HNSCC in a real-world setting.
Material/Methods
A retrospective chart review in a tertiary care facility in Ghent, Belgium, including all patients with LA HNSCC treated with concurrent cisplatin-based CRT, whether adjuvant or definite, from 2011-2022. Patients were treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) or volumetric-arc radiotherapy (VMAT) using simultaneous integrated boost. Definite treatment comprised 32x2.16 Gy to the primary tumor and involved lymph nodes, and 56 Gy to elective neck nodes. Adjuvant treatment comprised 32x2.16 Gy (after R1 or R2 resection or ENE) or 33x2Gy on tumor bed and 56 Gy on elective neck nodes. Patients who underwent neoadjuvant chemotherapy, had other histologic subtypes or who received prior irradiation for HNSCC were excluded. The primary outcomes were disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS). Secondary outcomes were 3-month locoregional control (LRC) measured as first response evaluation, treatment completion and grade 3-5 toxicity according to the CTCAE v5.0. Survival analyses were performed via the Kaplan-Meier method using the log-rank test. Independent outcomes were assessed at the 0.05 significance level.
Results
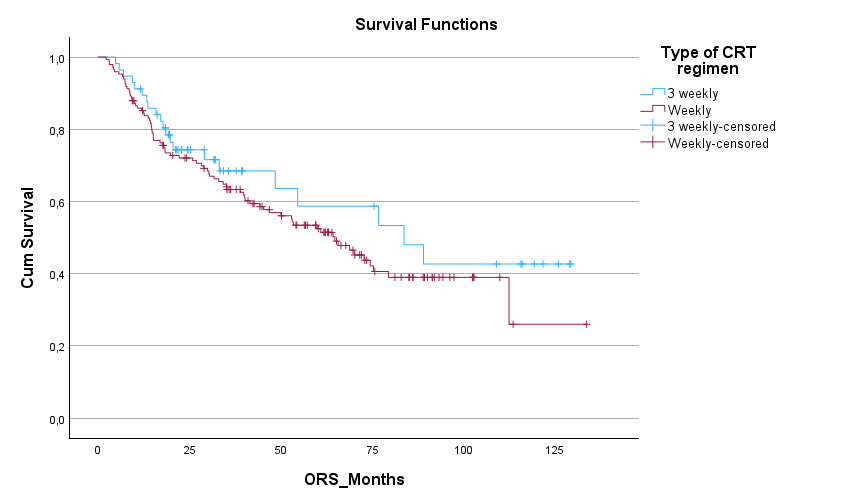
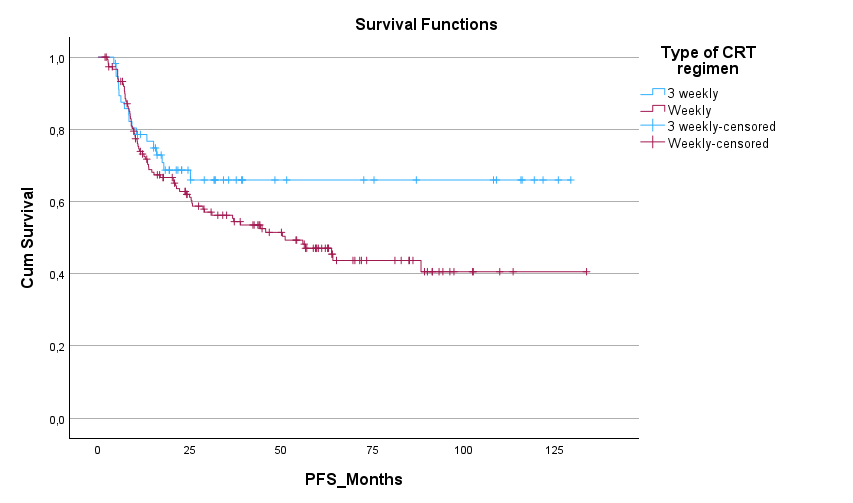
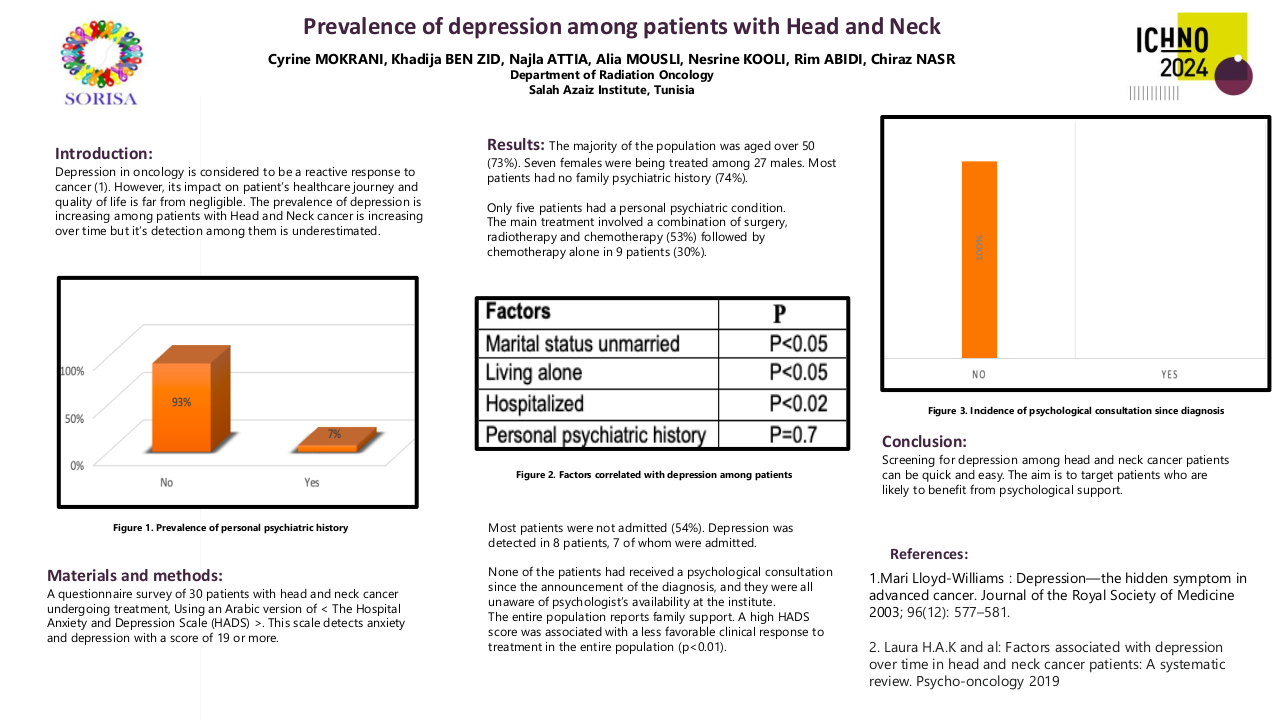
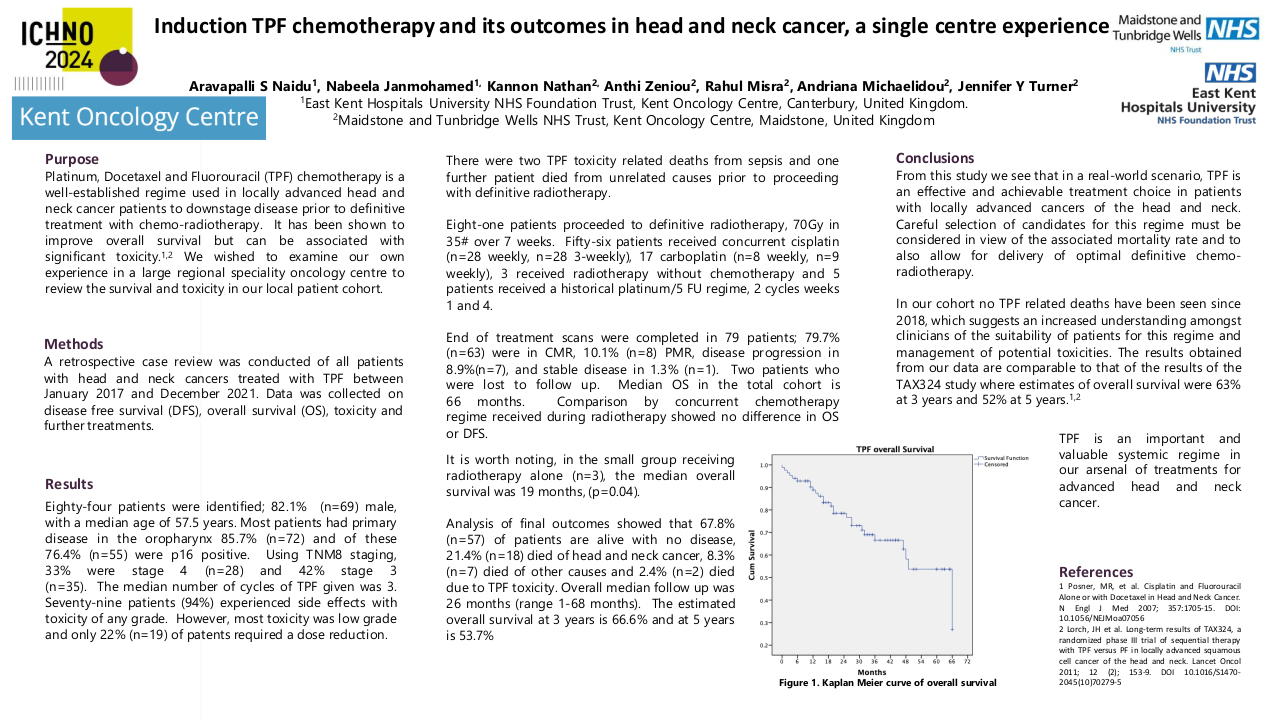
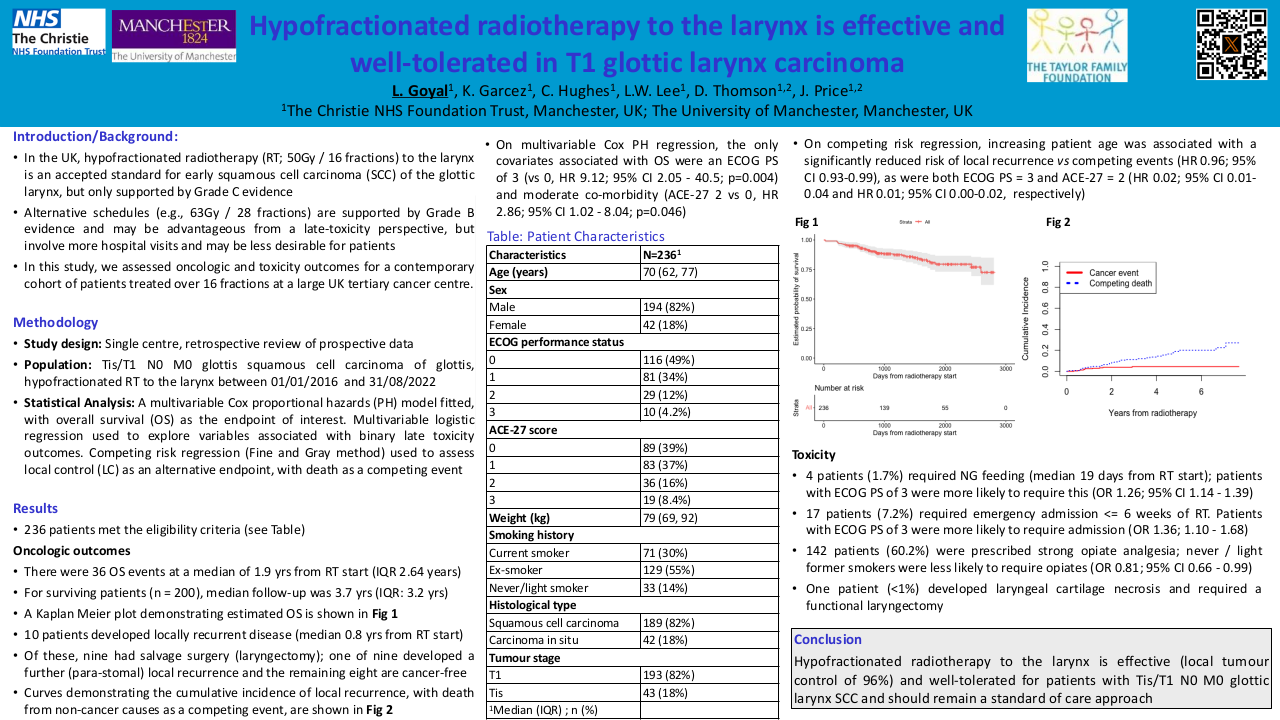
220 patients were included (162 cis40, 58 cis100). Median duration of follow-up was 66 months. Patient characterstics and outcomes are summarized in Table 1. Median OS and DFS were numerically longer in the cis100 group, although this difference was not statistically significant (mOS 83.6m vs 64.7m, p=0.316; mDFS NR vs 50.3m, p=0.125). First response evaluation showed no significant differences between the two groups (see table 1). Less patients completeted the full dose of prescribed radiotherapy in the cis40 group (93% vs 100%, p=0.07) although this was not significant. Mean cumulative dose of cisplatin was similar between groups. Toxicity analysis showed higher rates of ototoxicity (29 vs 7%, p<0.001) and gr 3-4 acute kidney failure (15.6vs 4.9%, p<0.05) and in the cis100 group, although this did not translate into increased chronic kidney impairment in the cis100 group. We observed more hematologic toxicity in the cis40 group (see table 1).
| Cisplatin 3-weekly (100mg/m²) N=58 |
Cisplatin weekly (40mg/m²) N=162 |
P value | |
| Mean age | 57.9 (SD 6.36) | 59.7 (SD 7.12) | |
| ECOG 0-1 2 NA |
16 (27%) 33 58%) 0 |
148 (91%) 12 (7%) 2 (2%) |
P=0.19 |
| Disease stage III IVa IVb |
16 (27%) 33 (58%) 9 (16%) |
28 (17%) 103 (63%) 31 (19%) |
P=0.24 |
| Primary Site oral cavity oropharynx P16+ P16- unknown hypopharynx larynx CUP |
14 (24%) 24 (41%) 9/24 9/24 6/24 9 (16%) 7 (12%) 4 (7%) |
45 (28%) 65 (40%) 19/65 24/65 22/65 27 (17%) 17 (10%) 8 (5%) |
P=0.96 |
| Indication for CRT adjuvant definite |
8 (14%) 50 (86%) |
36 (22%) 126 (78%) |
P=0.16 |
| Mean cumulative cisplatin dose | 233.4 mg/m² (IQR 100-300) | 231.7 mg/m² (IQR 200-280) | |
| Completion of prescribed RT | 58/58 (100%) | 151/162 (93%) | P=0.07 |
| mDFS | NR | 51.1 months [95%CI 30.4-71.7] | P=0.125 |
| mOS |
83.6 months [95%CI 40.8-125.1] | 64.7 [95%CI 49.5-79.9] | P=0.32 |
| First response evaluation CR PR PD/metastasis death NE |
42/58 (72%) 6/58 (10%) 5/58 (8%) 1/58 (2%) 4/58 (7%) |
110162 (67%) 26/162 (17%) 11/162 (7%) 3/162 (2%) 12/162 (7%) |
P=0.52 P=0.29 P=0.64 P=0.95 P=0.89 |
| Toxicity analysis | |||
| Gr 3-4 acute kidney injury | 9/58 (15.6%) | 8/162 (4.9%) | P<0.05 |
| Chronic kidney disease (>CKD gr3) | 1/58 (1.7%) | 5/162 (3%) | P=0.65 |
| Anemia (any grade) | 46/58 (79%) | 149/162 (92%) | P<0.05 |
| Anemia (gr 3-4) | 1/58 (1.6%) | 10/162 (6.1%) | P<0.05 |
| Neutropenia (gr 3-4) | 4/58 (7.8%) | 37/162 (22%) | P=0.16 |
| Febrile neutropenia | 1/58 (1.7%) | 4/162 (2.4%) | P=0.77 |
| Thrombocytopenia (gr 3-4) | 2/58 (3.4%) | 15/162 (9%) | P<0.05 |
| Mucositis gr 3-4 | 14/58 (24.1%) | 28/162 (17.2%) | P=0.172 |
| Acute hearing impairment (any grade) | 17/58 (29%) | 12/162 (7%) | P<0.001 |
| Acute hearing impairment (gr 3-4) | 9/58 (15%) | 5/162 (3%) | P<0.001 |
| Hospitalization during CRT | 21/58 (36%) | 76/162 (47%) | P=0.214 |
Conclusion
In this retrospective single-centre study, high dose cisplatin was associated with a trend to improved survival outcomes compared to weekly cisplatin. We observed an increase in Gr 3-4 acute kidney injury and ototoxicity in the cis-100 group, and more hematotoxicity in the cis40 group.