Real world data on Low-Dose Nivolumab with Triple Metronomic Chemotherapy: Retrospective analysis of 50 consecutive patients from LMICs
Purpose/Objective
In HNSCC, survival with chemotherapy is dismal in a palliative setting. In LMICs, access to cetuximab and IO is less than 3%.1 Therefore, treatment options are limited to chemotherapy. There is evidence suggesting that low-dose nivolumab, in combination with triple metronomic chemotherapy (TMC), improves OS.2 Yet, real-world data on the use of low-dose nivolumab remains scarce. This retrospective study aims to evaluate response rates associated with the combination of TMC and low-dose nivolumab in HNSCC patients.
Material/Methods
A retrospective analysis was conducted on 50 consecutive HNSCC patients with PS 0-1 who underwent combined TMC (Tab. Erlotinib 150mg once a day, Tab. Methotrexate 9mg/m² once a week, Cap. Celecoxib 200mg twice a day) and low-dose nivolumab(20 mg every 21 days) therapy from August 2022 to June 2023 with palliative intent(recurrent/metastatic/inoperable).Platinum sensitivity was defined as >6 months of gap from platinum exposure or platinum naive.
Descriptive statistics were performed for demographic details. Response assessments, including complete response (CR), partial response (PR), stable disease (SD), and progressive disease (PD), were conducted according to RECIST 1.1 criteria at 3 months. Response rate (RR) and clinical benefit rate (CBR) was calculated as per intention to treat.
Results
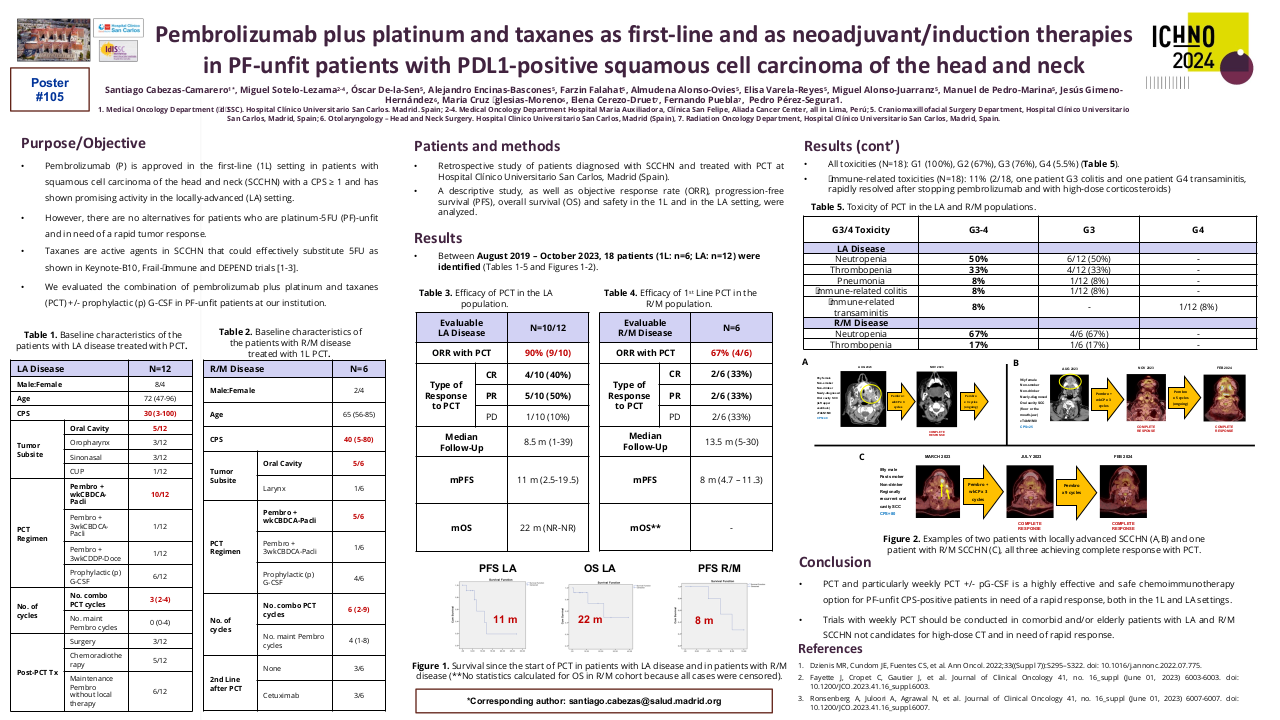
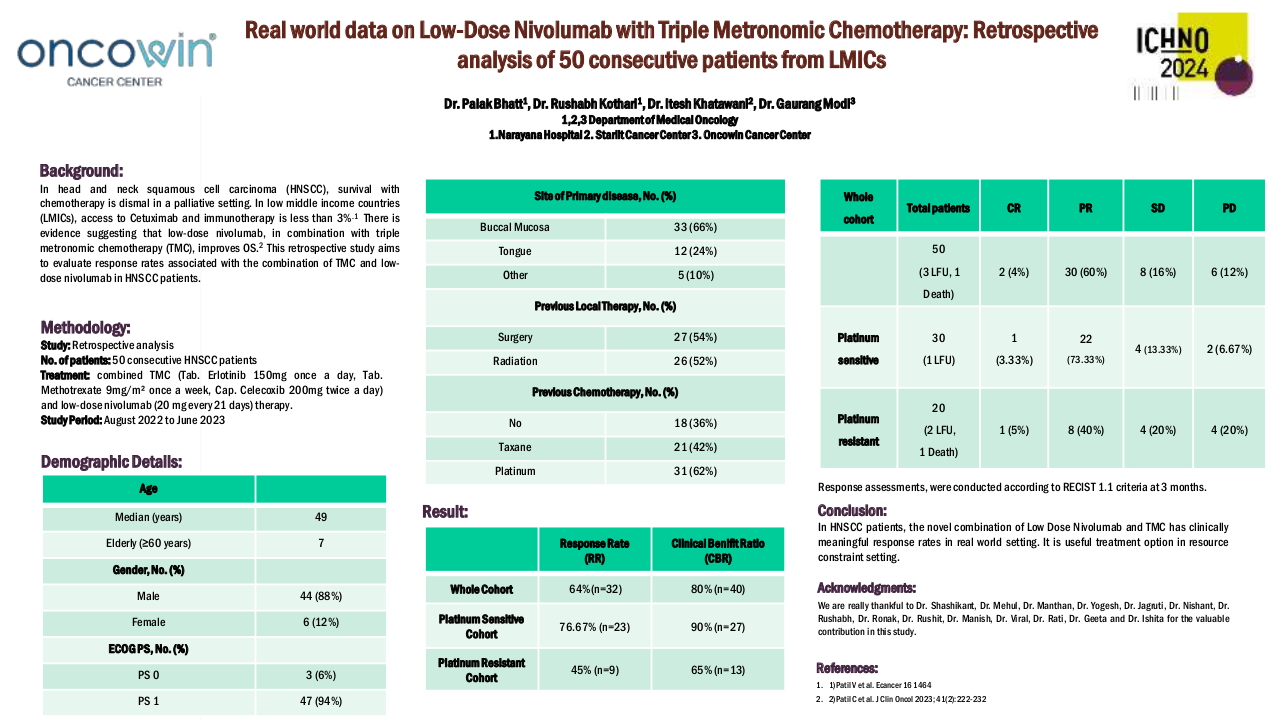
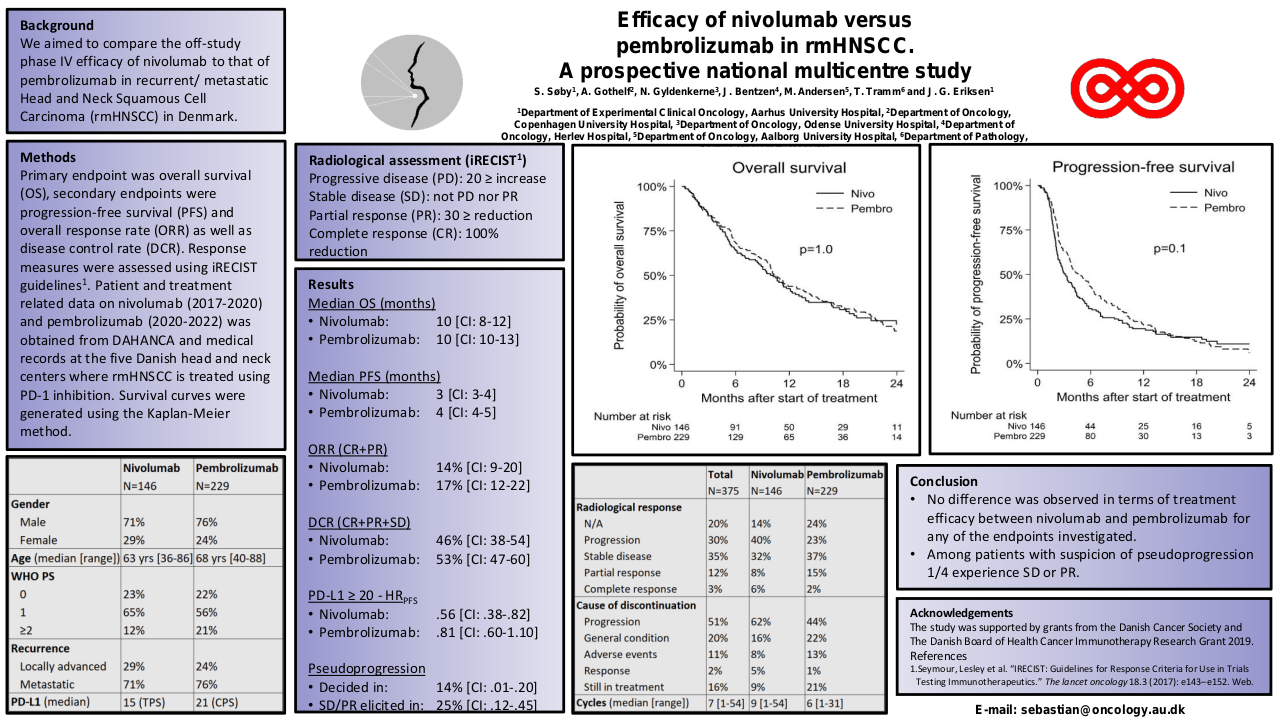
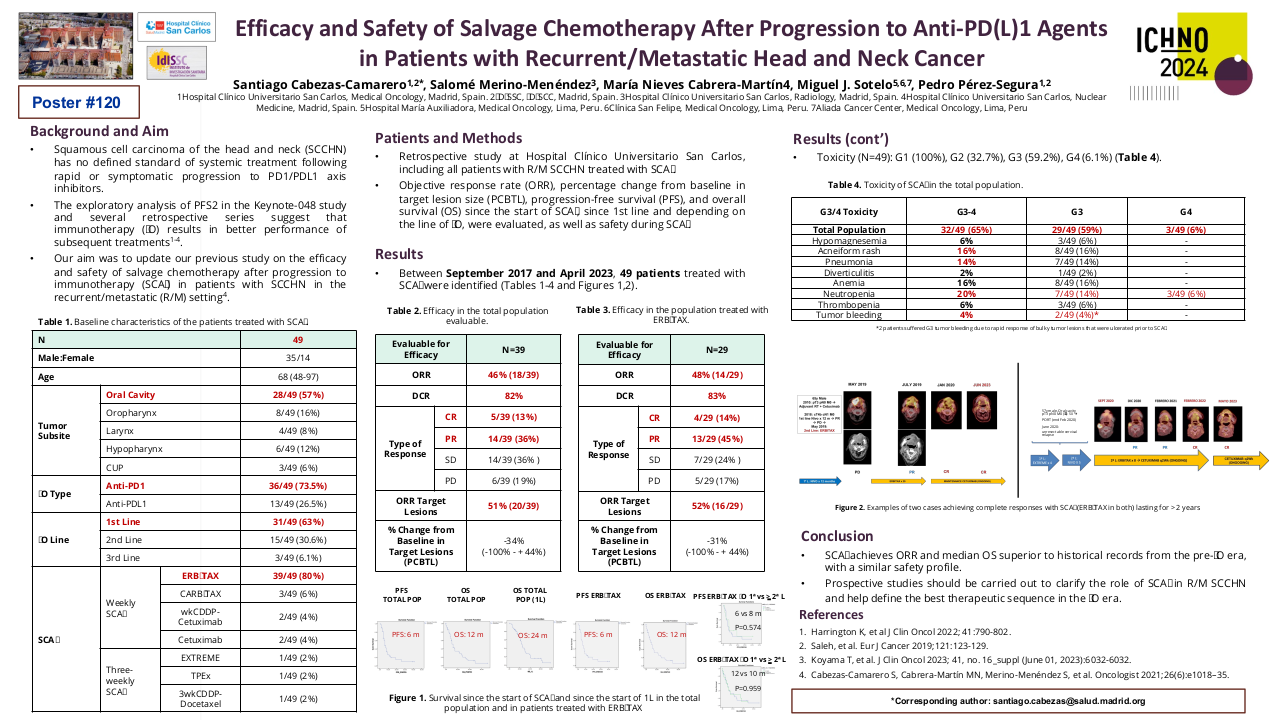
A total of 50 patients were included in this study, with 44 (88%) being male and 6 (12%) female. The median age was 49 years (35-78 years). ECOG PS-0 was observed in 3 (6%) patients, while 47 (94%) had ECOG PS-1. The primary site of malignancy was buccal mucosa in 33 (66%) patients, tongue in 12 (24%) patients, hard palate in 1 (2%) patient, and other primary sites in 4 (8%) patients. A history of surgery was present in 27 (54%) patients, and 26 (52%) had a history of radiation. 18 (36%) had no previous chemotherapy exposure. 31 (62%) had platinum exposure, and 21 (42%) had exposure to taxane. 30 (60%) were platinum-sensitive and 20 (40%) were platinum-resistant. In the whole cohort, 3 patients (1 in platinum sensitive and 2 in platinum resistant cohort) lost to follow up and 1 patient died (platinum resistant cohort).
In the whole cohort, the response rate (RR) was 64% (n=32), and the clinical benefit ratio (CBR) was 80% (n=40). RR and CBR in the platinum-sensitive cohort were 76.67% (n=23) and 90% (n=27) respectively. RR and CBR in the platinum-resistant cohort were 45% (n=9) and 65% (n=13) respectively.
| Whole Cohort | Total Patients | CR | PR | SD | PD |
| 50 (3 LUF, 1 Death) | 2 (4%) | 30 (60%) | 8 (16%) | 6 (12%) | |
| Platinum Sensitive | 30 (1 LUF) | 1 (3.33%) | 22 (73.33%) | 4 (13.33%) | 2 (6.67%) |
| Platinum Resistant | 20 (2 LUF, 1 Death) | 1 (5%) | 8 (40%) | 4 (20%) | 4 (20%) |
Conclusion
The novel combination of low dose nivolumab and TMC has clinically meaningful response rates in real world setting. It is useful options in resource constraint setting.
1. Patil V et al. Ecancer 16 14642. Patil V et al. J Clin Oncol 2023;41(2):222-232